Page 18 - ANUARIO
P. 18
riesgos lo que ha llevado a dejar de usar estos fármacos en esta patología. Se demuestra así que los
ensayos clínicos siguen siendo la mejor herramienta para guiar las decisiones de tratamiento incluso en
situaciones complejas como la que estamos viviendo en la pandemia Covid-19.
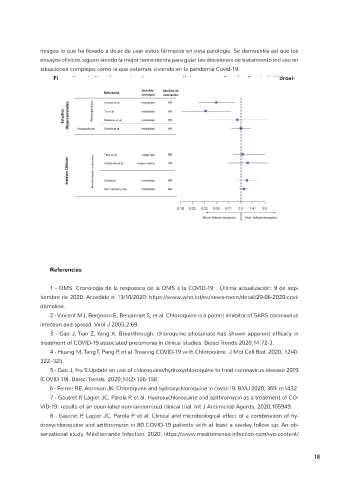
Figura 1 - estudios observacionales y ensayos clínicos que analizan la eficacia de hidroxi-
cloroquina en pacientes covid-19
Referencias
1 - OMS. Cronología de la respuesta de la OMS a la COVID-19●. Última actualización: 9 de sep-
tiembre de 2020. Accedido el 13/10/2020: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/detail/29-06-2020-covi-
dtimeline.
2 - Vincent MJ, Bergeron E, Benjannet S, et al. Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus
infection and spread. Virol J 2005;2:69.
3 - Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in
treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends 2020;14:72-3.
4 - Huang M, Tang T, Pang P, et al. Treating COVID-19 with Chloroquine. J Mol Cell Biol. 2020; 12(4):
322–325.
5 - Gao J, Hu S.Update on use of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine to treat coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19). Biosci Trends. 2020;14(2):156-158.
6 - Ferner RE, Aronson JK. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in covid-19. BMJ 2020; 369: m1432.
7 - Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of CO-
VID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;105949.
8 - Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, et al. Clinical and microbiological effect of a combination of hy-
droxychloroquine and azithromycin in 80 COVID-19 patients with at least a six-day follow up: An ob-
servational study. Méditerranée Infection. 2020. https://www.mediterranee-infection.com/wp-content/
18