Page 29 - UMH Sapiens 38
P. 29
Science for Sapiens A year in research (2024)
he Laboratory for Red Blood Cells in An-
tiviral Immunology of the Institute for Re-
search, Development and Innovation in
Sanitary Biotechnology of Elche (IDiBE) of
the University Miguel Hernández (UMH)
of Elche, led by researcher María del Mar
Ortega-Villaizán, conducts experiments
T on the red blood cells of fish, also called
red blood cells, in the ALBA Synchrotron, where UMH Alumni 1
Ana Joaquina Pérez Bera is a scientist of the MISTRAL light
line. A synchrotron is an infrastructure that accelerates elec-
trons at speeds close to that of light. By moving this fast, elec-
trons emit a specific type of light, synchrotron light, which is
used to study matter at very small scales. If you want to know
more, we’ll explain how this facility helps to shed light on the
future of fish consumption on the planet.
Most of the fish we consume does not come from open sea
fishing. It is grown in fish farms, where the viral infections su- 2
ffered by fish are a serious problem because fish infect each
other quickly and die. In the case of humans, we know a lot
about our immune system, about how different cells in the
body react to infections, and what we can do to fight them.
However, in the case of fish, we still do not know enough
about their immune system. Giving them drugs is not good
for the environment or for consumption. In addition, there
are no fully effective treatments for viral infections, so scien-
ce is trying to find vaccines or other treatments that prevent
or stop viral infections in fish farms. 3
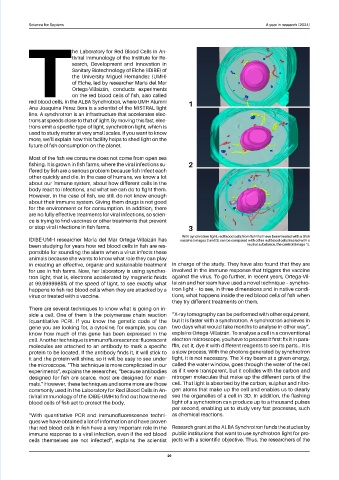
With synchrotron light, red blood cells from fish that have been treated with a DNA
IDiBE-UMH researcher María del Mar Ortega-Villaizán has vaccine [Images 2 and 3] can be compared with other red blood cells treated with a
been studying for years how red blood cells in fish are res- neutral substance, the control [Image 1].
ponsible for sounding the alarm when a virus infects these
animals because she wants to know what role they can play
in creating an effective, organic and sustainable treatment in charge of the study. They have also found that they are
for use in fish farms. Now, her laboratory is using synchro- involved in the immune response that triggers the vaccine
tron light, that is, electrons accelerated by magnetic fields against the virus. To go further, in recent years, Ortega-Vil-
at 99.9999985% of the speed of light, to see exactly what laizán and her team have used a novel technique – synchro-
happens to fish red blood cells when they are attacked by a tron light – to see, in three dimensions and in native condi-
virus or treated with a vaccine. tions, what happens inside the red blood cells of fish when
they try different treatments on them.
There are several techniques to know what is going on in-
side a cell. One of them is the polymerase chain reaction “X-ray tomography can be performed with other equipment,
(quantitative PCR). If you know the genetic code of the but it is faster with a synchrotron. A synchrotron achieves in
gene you are looking for, a cytokine, for example, you can two days what would take months to analyse in other way”,
know how much of this gene has been expressed in the explains Ortega-Villaizán. To analyse a cell in a conventional
cell. Another technique is immunofluorescence: fluorescent electron microscope, you have to process it first: fix it in para-
molecules are attached to an antibody to mark a specific ffin, cut it, dye it with different reagents to see its parts… It is
protein to be located. If the antibody finds it, it will stick to a slow process. With the photons generated by synchrotron
it and the protein will shine, so it will be easy to see under light, it is not necessary. The X-ray beam at a given energy,
the microscope. “This technique is more complicated in our called the water window, goes through the water of the cell
experiments”, explains the researcher, “because antibodies as if it were transparent, but it collides with the carbon and
designed for fish are scarce, most are designed for mam- nitrogen molecules that make up the different parts of the
mals.” However, these techniques and some more are those cell. That light is absorbed by the carbon, sulphur and nitro-
commonly used in the Laboratory for Red Blood Cells in An- gen atoms that make up the cell and enables us to clearly
tiviral Immunology of the IDiBE-UMH to find out how the red see the organelles of a cell in 3D. In addition, the flashing
blood cells of fish act to protect the body. light of a synchrotron can produce up to a thousand pulses
per second, enabling us to study very fast processes, such
“With quantitative PCR and immunofluorescence techni- as chemical reactions.
ques we have obtained a lot of information and have proven
that red blood cells in fish have a very important role in the Research grant at the ALBA Synchrotron funds the studies by
immune response to a viral infection, even if the red blood public institutions that want to use synchrotron light for pro-
cells themselves are not infected”, explains the scientist jects with a scientific objective. Thus, the researchers of the
29